The release of Docker for Windows Stable version 18.06..0-ce-win70 comes with some great new features I looked for a while including the K8s support! That’s a pretty good news because this support has existed on Edge channel since the beginning of this year but no chance to install a beta version on my laptop from my side.
So, we get now a good opportunity to test locally our SQL Server image with a K8s single node architecture.
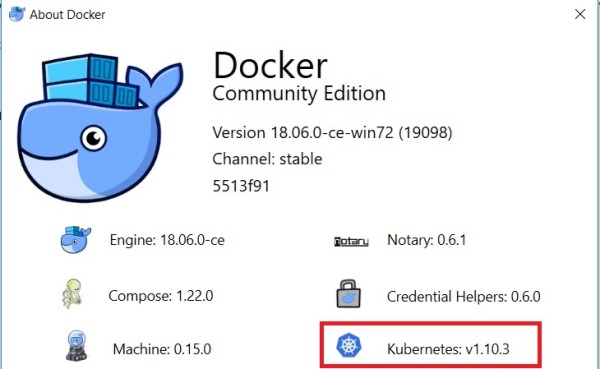
One interesting point here is I may switch the context of K8s infrastructure as shown below:
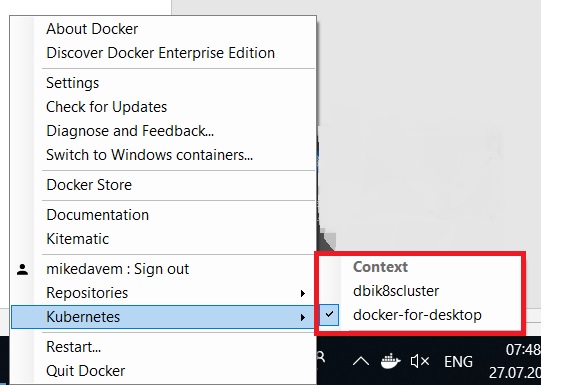
The first one (dbi8scluster) corresponds to my K8s cluster on Azure. I wrote about it some time ago and the second one is about my single K8s node on my Windows 10 laptop. So, switching to my different environments is very easy as shown below:
[dab@DBI:$]> kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION aks-nodepool1-78763348-0 NotReady agent 57d v1.9.6 aks-nodepool1-78763348-1 NotReady agent 57d v1.9.6 C:\Users\dab\Desktop [dab@DBI:$]> kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION docker-for-desktop Ready master 1d v1.10.3 C:\Users\dab\Desktop
It is also interesting to get a picture of the container installed and that run the K8s infrastructure on Docker. Assuming you already enabled the showing system containers option in advanced mode you may display all the K8s related containers as following:
[dab@DBI:$]> docker ps --format "table {{.ID}}\t {{.Names}}"
CONTAINER ID NAMES
829a5941592e k8s_compose_compose-7447646cf5-l5shp_docker_7e3ff6d9-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
53666469f25d k8s_compose_compose-api-6fbc44c575-7jrj8_docker_7e3ff0d0-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
cd3772216e72 k8s_sidecar_kube-dns-86f4d74b45-v7mr9_kube-system_7e3cb79b-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
8ae73505dfb0 k8s_dnsmasq_kube-dns-86f4d74b45-v7mr9_kube-system_7e3cb79b-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
8066fbefc371 k8s_kubedns_kube-dns-86f4d74b45-v7mr9_kube-system_7e3cb79b-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
2591d102e6fb k8s_kube-proxy_kube-proxy-p9jv9_kube-system_7e43eaab-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
80f6d997a225 k8s_POD_compose-7447646cf5-l5shp_docker_7e3ff6d9-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
23751c4fd2fc k8s_POD_kube-proxy-p9jv9_kube-system_7e43eaab-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
f96406dedefb k8s_POD_compose-api-6fbc44c575-7jrj8_docker_7e3ff0d0-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
9149e9b91fd3 k8s_POD_kube-dns-86f4d74b45-v7mr9_kube-system_7e3cb79b-908e-11e8-91f0-00155d0013a6_4
2316ed63e2ee k8s_kube-controller-manager_kube-controller-manager-docker-for-desktop_kube-system_120c685a17dc3d67e505450a6ea9243c_4
52defb42bbaf k8s_kube-apiserver_kube-apiserver-docker-for-desktop_kube-system_814863b48e4b523c13081a7bb4c85f0d_4
3366ebf8f058 k8s_kube-scheduler_kube-scheduler-docker-for-desktop_kube-system_ea66a171667ec4aaf1b274428a42a7cf_4
bd903b9dce3f k8s_etcd_etcd-docker-for-desktop_kube-system_d82203d846b07255217d0e72211752f0_4
7e650673b6d2 k8s_POD_kube-apiserver-docker-for-desktop_kube-system_814863b48e4b523c13081a7bb4c85f0d_4
24e4bfb59184 k8s_POD_kube-scheduler-docker-for-desktop_kube-system_ea66a171667ec4aaf1b274428a42a7cf_4
3422edb44165 k8s_POD_etcd-docker-for-desktop_kube-system_d82203d846b07255217d0e72211752f0_4
aeca6879906b k8s_POD_kube-controller-manager-docker-for-desktop_kube-system_120c685a17dc3d67e505450a6ea9243c_4
We retrieve all the K8s components including the API server, the controller manager, the K8s scheduler, the kube-proxy and the etcd cluster database. It is not my intention to go further on this topic and I will probably get the opportunity to dig further in the next blog posts.
My first test consisted in deploying our dbi services custom image for development about SQL Server 2017 Linux on my K8s cluster node. I already did it with our dbi services production image on my previous K8s infrastructure on Azure and it could be interesting to check if we have to operate in the same way. This is at least what I expected and I was right. Just note I didn’t perform the same test with Windows containers yet but it will be soon hopefully.
Obviously, I had to change my storage classes to StorageClassName = hostpath to point to my host storage as follows:
kind: PersistentVolume
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: pv-data-sql
labels:
type: local
spec:
storageClassName: hostpath
capacity:
storage: 10Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
hostPath:
path: /T/Docker/DMK/BACKUP
---
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: pv-claim-data-sql
spec:
storageClassName: hostpath
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
I just want to draw your attention to the hostPath because we have to apply some modifications from the initial path to be understood by K8s. On Windows side my path is T:/Docker/DMK/BACKUP and it contains a backup of my custom AdventureWorks database for our tests.
Here the command to deploy my persistence volume and the correspond persistent volume claim that will be used by my SQL Server pod:
[dab@DBI:$]> kubectl create -f .\docker_k8s_storage.yaml persistentvolume "pv-data-sql" created persistentvolumeclaim "pv-claim-data-sql" created
Then my development file didn’t change a lot as expected:
apiVersion: apps/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mssql-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mssql
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10
volumes:
- name: mssqldb
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pv-claim-data-sql
containers:
- name: mssql
image: dbi/dbi_linux_sql2017:2017-CU4
ports:
- containerPort: 1433
env:
- name: ACCEPT_EULA
value: "Y"
- name: MSSQL_SA_PASSWORD
value: "Password1"
# valueFrom:
# secretKeyRef:
# name: mssql
# key: SA_PASSWORD
- name: DMK
value: "Y"
volumeMounts:
- name: mssqldb
mountPath: "/backup"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mssql-deployment
spec:
selector:
app: mssql
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 1433
targetPort: 1433
type: LoadBalancer
The command to deploy my SQL Server container pod and the correspond service is:
[dab@DBI:$]> kubectl create -f .\docker_k8s_sql.yaml deployment.apps "mssql-deployment" created service "mssql-deployment" created
So, let’s get a picture of my new deployed environment:
[dab@DBI:$]> kubectl get deployments NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE mssql-deployment 1 1 1 1 2m [dab@DBI:$]> kubectl get services NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 1d mssql-deployment LoadBalancer 10.109.238.88 localhost 1433:30200/TCP 2m [dab@DBI:$]> kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE mssql-deployment-6c69bb6f7c-pqb2d 1/1 Running 0 7m 10.1.0.39 docker-for-desktop
Everything seems to be deployed successfully. I use a load balancer service here but bear in mind I just have only one node. Here a description of my new deployed pod:
[dab@DBI:$]> kubectl describe pod mssql-deployment-6c69bb6f7c-pqb2d
Name: mssql-deployment-6c69bb6f7c-pqb2d
Namespace: default
Node: docker-for-desktop/192.168.65.3
Start Time: Fri, 27 Jul 2018 12:45:50 +0200
Labels: app=mssql
pod-template-hash=2725662937
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.1.0.39
Controlled By: ReplicaSet/mssql-deployment-6c69bb6f7c
Containers:
mssql:
Container ID: docker://a17039dcdcb22c1b4b80c73fb17e73df90efda19ed77e215ef92bf86c9bfc538
Image: dbi/dbi_linux_sql2017:2017-CU4
Image ID: docker://sha256:2a693c121c33c390f944df7093b8c902f91940fa966ae8e5190a7a4a5b0681d2
Port: 1433/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Fri, 27 Jul 2018 12:45:51 +0200
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment:
ACCEPT_EULA: Y
MSSQL_SA_PASSWORD: Password1
DMK: Y
Mounts:
/backup from mssqldb (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-5qts2 (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
mssqldb:
Type: PersistentVolumeClaim (a reference to a PersistentVolumeClaim in the same namespace)
ClaimName: pv-claim-data-sql
ReadOnly: false
default-token-5qts2:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-5qts2
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 3m default-scheduler Successfully assigned mssql-deployment-6c69bb6f7c-pqb2d to docker-for-desktop
Normal SuccessfulMountVolume 3m kubelet, docker-for-desktop MountVolume.SetUp succeeded for volume "pv-data-sql"
Normal SuccessfulMountVolume 3m kubelet, docker-for-desktop MountVolume.SetUp succeeded for volume "default-token-5qts2"
Normal Pulled 3m kubelet, docker-for-desktop Container image "dbi/dbi_linux_sql2017:2017-CU4" already present on machine
Normal Created 3m kubelet, docker-for-desktop Created container
Normal Started 3m kubelet, docker-for-desktop Started container
And finally, let’s have a look at a sample of my SQL Server log:
========================== 2018-07-27 10:46:43 Restoring AdventureWorks database OK ========================== ========================== 2018-07-27 10:46:43 Installing TSQLt ========================== 2018-07-27 10:46:44.01 spid51 Configuration option 'show advanced options' changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. Configuration option 'show advanced options' changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. 2018-07-27 10:46:44.02 spid51 Configuration option 'clr enabled' changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. 2018-07-27 10:46:44.02 spid51 Configuration option 'clr strict security' changed from 1 to 0. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. 2018-07-27 10:46:44.02 spid51 Configuration option 'max server memory (MB)' changed from 2147483647 to 3072. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. Configuration option 'clr enabled' changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. Configuration option 'clr strict security' changed from 1 to 0. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. Configuration option 'max server memory (MB)' changed from 2147483647 to 3072. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. 2018-07-27 10:46:47.39 spid51 Starting up database 'dbi_tools'. 2018-07-27 10:46:47.72 spid51 Parallel redo is started for database 'dbi_tools' with worker pool size [2]. 2018-07-27 10:46:47.74 spid51 Parallel redo is shutdown for database 'dbi_tools' with worker pool size [2]. Installed at 2018-07-27 10:46:47.863 2018-07-27 10:46:48.54 spid51 AppDomain 3 (dbi_tools.dbo[runtime].2) created. (1 rows affected) +-----------------------------------------+ | | | Thank you for using tSQLt. | | | | tSQLt Version: 1.0.5873.27393 | | | +-----------------------------------------+ 0 ========================== 2018-07-27 10:46:49 Installing TSQLt OK ========================== ======= 2018-07-27 10:46:49 MSSQL CONFIG COMPLETED ======= 2018-07-27 10:51:03.35 spid55 Using 'dbghelp.dll' version '4.0.5' 2018-07-27 10:51:10.32 spid55 Attempting to load library 'xplog70.dll' into memory. This is an informational message only. No user action is required. 2018-07-27 10:51:10.40 spid55 Using 'xplog70.dll' version '2017.140.3022' to execute extended stored procedure 'xp_msver'. This is an informational message only; no user action is required.
My SQL Server pod is mounted with my restored AdventureWorks database accessible from my /backup path inside my container. We also added to the image, the tSQLt framework for our unit tests.
Let’s connect to my SQL Server pod by using mssql-cli CLI:
C:\WINDOWS\system32>mssql-cli -S localhost -U sa -P Password1 Version: 0.15.0 Mail: [email protected] Home: http://github.com/dbcli/mssql-cli master> Time: 0.000s master> select name from sys.databases; +--------------------+ | name | |--------------------| | master | | tempdb | | model | | msdb | | AdventureWorks_dbi | | dbi_tools | +--------------------+ (6 rows affected) Time: 0.406s
My first deployment is successful. There are plenty of topics to cover about K8s and SQL Server containers and other writes-up will come soon for sure. Stay tuned!
By David Barbarin
![Thumbnail [60x60]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/microsoft-square.png)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/STS_web-min-scaled.jpg)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/STH_web-min-scaled.jpg)