By Mouhamadou Diaw
Edb Failover Manager edb-efm30 is now released and supports PostgreSQL 10.1.
Efm is an EDB tool which can be used to perform a switchover and a failover in a PostgreSQL standby environment.
In this blog we are going to see how we can install and configure efm in a standby environment. We suppose that the standby is already confugured and is running. We also have not configured any VIP. I just use 3 virtual machines to test. Below the configuration we are using 3 servers with Oracle Linux 7.2
pgservertools: 192.168.56.30 which is the witness
pgserver1: 192.168.56.36 which is the primary server
pgserver2: 192.168.56.37 which is the standby
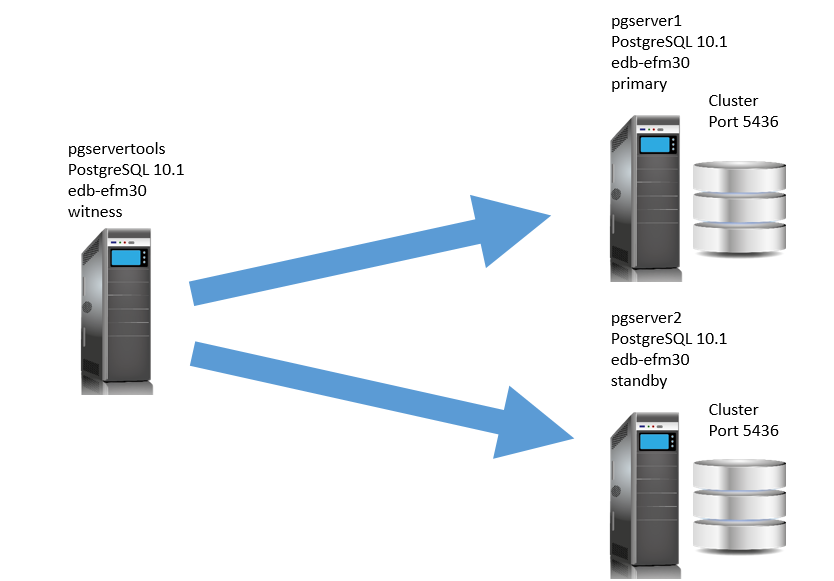
EFM must be installed on both 3 nodes.To install EDB EFM,I used the rpm provided by EnterpriseDB. Note that you will need an Edb account.We will show the installation on only one node, but is the same for both nodes.
|
1
2
|
[root@host tmp]# wget http://yum.enterprisedb.com/edbrepos/edb-repo-latest.noarch.rpm[root@host tmp]# yum localinstall -y edb-repo-latest.noarch.rpm |
After we have to enable the corresponding edb repository (You will need a login and password)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
[root@pgservertools yum.repos.d]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/edb.repo[edbas10]name=EnterpriseDB Advanced Server 10 $releasever - $basearchenabled=1gpgcheck=1gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/ENTERPRISEDB-GPG-KEY |
And then we can search for the package
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@pgservertools ~]# yum search efmLoaded plugins: langpacks, ulninfo=============================== N/S matched: efm ===============================edb-efm30.x86_64 : EnterpriseDB Failover Managerefm20.x86_64 : EnterpriseDB Failover Managerefm21.x86_64 : EnterpriseDB Failover Manager |
And then install it (ouputs are truncated)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
[root@pgservertools ~]# yum install edb-efm30.x86_64Loaded plugins: langpacks, ulninfoResolving Dependencies--> Running transaction check---> Package edb-efm30.x86_64 0:3.0.0-1.rhel7 will be installed--> Finished Dependency Resolution……Installed: edb-efm30.x86_64 0:3.0.0-1.rhel7Complete! |
efm requires also openjdk. So we also have installed openjdk 1.8 on all nodes:
|
1
|
root@host tmp]# yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64 |
To manage efm we create a dedicated user in the primary cluster
|
1
2
3
|
postgres=# create user efm with login password 'root' superuser;CREATE ROLEpostgres=# |
We have to add following entries to pg_hba.conf of all databases clusters to allow connection for user efm.
|
1
2
3
4
|
##for efmhost postgres efm 192.168.56.36/32 md5host postgres efm 192.168.56.37/32 md5host postgres efm 192.168.56.30/32 md5 |
The configuration of efm consists of editing 2 main configuration files: efm.nodes and efm.properties. In my case these files are located in /etc/edb/efm-3.0. There are already two sample files that we can copy and then edit.
First we need to encrypt the password of user efm and after we have to configure efm.nodes and efm.properties on both nodes.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
[root@pgserver1 efm-3.0]# /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/efm encrypt efmThis utility will generate an encrypted password for you to place in yourEFM cluster property file.Please enter the password and hit enter:Please enter the password again to confirm:The encrypted password is: ff7f041651e5e864013c1102d26a5e08Please paste this into your cluster properties file. db.password.encrypted= ff7f041651e5e864013c1102d26a5e08 |
Below we show the contents of our two configuration files
On pgserver1 which is the primary
efm.nodes
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
root@pgserver1 101]# cat /etc/edb/efm-3.0/efm.nodes# List of node address:port combinations separated by whitespace.# The list should include at least the membership coordinator's address.192.168.56.30:9998 192.168.56.37:9998[root@pgserver1 101]# |
efm.properties
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
[root@pgserver1 101]# cat /etc/edb/efm-3.0/efm.properties | grep -v ^#db.user=efmdb.password.encrypted=ff7f041651e5e864013c1102d26a5e08db.port=5436db.database=postgresdb.service.owner=postgresdb.service.name=db.bin=/u01/app/postgres/product/10/db_1/bindb.recovery.conf.dir=/u90/mydata/101jdbc.sslmode=disablescript.notification=bind.address=192.168.56.36:9998admin.port=9999is.witness=falselocal.period=10local.timeout=60local.timeout.final=10remote.timeout=10node.timeout=50stop.isolated.master=falsepingServerIp=192.168.56.30pingServerCommand=/bin/ping -q -c3 -w5auto.allow.hosts=falsedb.reuse.connection.count=0auto.failover=trueauto.reconfigure=truepromotable=trueminimum.standbys=0recovery.check.period=2auto.resume.period=0script.fence=script.post.promotion=script.resumed=script.db.failure=script.master.isolated=script.remote.pre.promotion=script.remote.post.promotion=script.custom.monitor=custom.monitor.interval=custom.monitor.timeout=custom.monitor.safe.mode=sudo.command=sudosudo.user.command=sudo -u %ulog.dir=/var/log/efm-3.0jgroups.loglevel=INFOefm.loglevel=INFOjvm.options=-Xmx32m[root@pgserver1 101]# |
On pgserver2 which is the standby
efm.nodes
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@pgserver2 tmp]# cat /etc/edb/efm-3.0/efm.nodes# List of node address:port combinations separated by whitespace.# The list should include at least the membership coordinator's address.192.168.56.30:9998 192.168.56.36:9998[root@pgserver2 tmp]# |
efm.properties
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
[root@pgserver2 tmp]# cat /etc/edb/efm-3.0/efm.properties | grep -v ^#db.user=efmdb.password.encrypted=ff7f041651e5e864013c1102d26a5e08db.port=5436db.database=postgresdb.service.owner=postgresdb.service.name=db.bin=/u01/app/postgres/product/10/db_1/bindb.recovery.conf.dir=/u90/mydata/101jdbc.sslmode=disablescript.notification=bind.address=192.168.56.37:9998admin.port=9999is.witness=falselocal.period=10local.timeout=60local.timeout.final=10remote.timeout=10node.timeout=50stop.isolated.master=falsepingServerIp=192.168.56.30pingServerCommand=/bin/ping -q -c3 -w5auto.allow.hosts=truedb.reuse.connection.count=0auto.failover=trueauto.reconfigure=truepromotable=trueminimum.standbys=0recovery.check.period=2auto.resume.period=0script.fence=script.post.promotion=script.resumed=script.db.failure=script.master.isolated=script.remote.pre.promotion=script.remote.post.promotion=script.custom.monitor=custom.monitor.interval=custom.monitor.timeout=custom.monitor.safe.mode=sudo.command=sudosudo.user.command=sudo -u %ulog.dir=/var/log/efm-3.0jgroups.loglevel=INFOefm.loglevel=INFOjvm.options=-Xmx32m[root@pgserver2 tmp]# |
On pgservertools which is the witness
efm.nodes
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# cat /etc/edb/efm-3.0/efm.nodes# List of node address:port combinations separated by whitespace.# The list should include at least the membership coordinator's address.192.168.56.36:9998 192.168.56.37:9998[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# |
efm.properties
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# cat /etc/edb/efm-3.0/efm.properties | grep -v ^#db.user=efmdb.password.encrypted=ff7f041651e5e864013c1102d26a5e08db.port=5436db.database=postgresdb.service.owner=postgresdb.service.name=db.bin=/u01/app/postgres/product/10/db_1/bindb.recovery.conf.dir=/u90/mydata/101jdbc.sslmode=disablescript.notification=bind.address=192.168.56.30:9998admin.port=9999is.witness=truelocal.period=10local.timeout=60local.timeout.final=10remote.timeout=10node.timeout=50stop.isolated.master=falsepingServerIp=192.168.56.30pingServerCommand=/bin/ping -q -c3 -w5auto.allow.hosts=falsedb.reuse.connection.count=0auto.failover=trueauto.reconfigure=truepromotable=trueminimum.standbys=0recovery.check.period=2auto.resume.period=0script.fence=script.post.promotion=script.resumed=script.db.failure=script.master.isolated=script.remote.pre.promotion=script.remote.post.promotion=script.custom.monitor=custom.monitor.interval=custom.monitor.timeout=custom.monitor.safe.mode=sudo.command=sudosudo.user.command=sudo -u %ulog.dir=/var/log/efm-3.0jgroups.loglevel=INFOefm.loglevel=INFOjvm.options=-Xmx32m[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# |
Now let’s start efm on both nodes. If there is any error check logs on /var/log/efm-3.0/.
I started on following order: pgserver1, pgserver2 and pgservertools. Services can be configured to be started automatically when the server starts.
Below an example on pgserverools
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# service efm-3.0 start.[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# service efm-3.0 statusRedirecting to /bin/systemctl status efm-3.0.service● efm-3.0.service - EnterpriseDB Failover Manager 3.0 Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/efm-3.0.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2018-03-06 15:58:51 CET; 1h 46min ago Process: 22260 ExecStart=/bin/bash -c /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/runefm.sh start ${CLUSTER} (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 22321 (java) CGroup: /system.slice/efm-3.0.service └─22321 /usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.151-1.b12.el7_4.x86_64/jre/bin/java -cp /usr/edb/efm-3.0/lib/EFM-3.0.0.jar -Xmx32m com.enterprisedb.efm.main.ServiceCommand __int_start /e...Mar 06 15:58:45 pgservertools.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting EnterpriseDB Failover Manager 3.0...Mar 06 15:58:51 pgservertools.localdomain systemd[1]: Started EnterpriseDB Failover Manager 3.0.[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# |
Once started we can verified from any node the status of our cluster
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/efm cluster-status efmCluster Status: efmVIP: Agent Type Address Agent DB Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Witness 192.168.56.30 UP N/A Master 192.168.56.36 UP UP Standby 192.168.56.37 UP UPAllowed node host list: 192.168.56.36 192.168.56.37 192.168.56.30Membership coordinator: 192.168.56.30Standby priority host list: 192.168.56.37Promote Status: DB Type Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Master 192.168.56.36 0/430001A8 Standby 192.168.56.37 0/430001A8 Standby database(s) in sync with master. It is safe to promote.[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# |
Now that everything is ok, let’s do a switchover
|
1
2
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/efm promote efm -switchoverPromote/switchover command accepted by local agent. Proceeding with promotion and will reconfigure original master. Run the 'cluster-status' command for information about the new cluster state. |
And if we run the cluster-status command during the switchover
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/efm cluster-status efmCluster Status: efmVIP: Agent Type Address Agent DB Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Witness 192.168.56.30 UP N/A Idle 192.168.56.36 UP UNKNOWN Standby 192.168.56.37 UP UPAllowed node host list: 192.168.56.36 192.168.56.37 192.168.56.30Membership coordinator: 192.168.56.30Standby priority host list: 192.168.56.37Promote Status: DB Type Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Standby 192.168.56.37 0/44000098 No master database was found.Idle Node Status (idle nodes ignored in XLog location comparisons): Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- 192.168.56.36 UNKNOWN Connection to 192.168.56.36:5436 refused. Check that the hostname and port are correct and that the postmaster is accepting TCP/IP connections. |
And we can see the promoting phase
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/efm cluster-status efmCluster Status: efmVIP: Agent Type Address Agent DB Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Witness 192.168.56.30 UP N/A Idle 192.168.56.36 UP UNKNOWN Promoting 192.168.56.37 UP UPAllowed node host list: 192.168.56.36 192.168.56.37 192.168.56.30Membership coordinator: 192.168.56.30Standby priority host list: (List is empty.)Promote Status: DB Type Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Master 192.168.56.37 0/44000170 No standby databases were found.Idle Node Status (idle nodes ignored in XLog location comparisons): Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- 192.168.56.36 UNKNOWN Connection to 192.168.56.36:5436 refused. Check that the hostname and port are correct and that the postmaster is accepting TCP/IP connections. |
And after a few time we can see that the new master is on pgserver2
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/efm cluster-status efmCluster Status: efmVIP: Agent Type Address Agent DB Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Witness 192.168.56.30 UP N/A Standby 192.168.56.36 UP UP Master 192.168.56.37 UP UPAllowed node host list: 192.168.56.36 192.168.56.37 192.168.56.30Membership coordinator: 192.168.56.30Standby priority host list: 192.168.56.36Promote Status: DB Type Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Master 192.168.56.37 0/440001A8 Standby 192.168.56.36 0/440001A8 Standby database(s) in sync with master. It is safe to promote.[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# |
The purpose of the witness is to do an automatic failover when the primary is down. Let’s simulate a crash of our primary database by killing the corresponding process.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
[root@pgserver2 tmp]# ps -ef | grep postgres......root 17529 14103 0 16:45 pts/1 00:00:00 tail -f /u90/mydata/101/log/postgresql-2018-03-06.log<strong>postgres 20612 1 0 17:56 ? 00:00:00 /u01/app/postgres/product/10/db_1/bin/postgres -D /u90/mydata/101</strong>postgres 20613 20612 0 17:56 ? 00:00:00 postgres: logger processpostgres 20615 20612 0 17:56 ? 00:00:00 postgres: checkpointer processpostgres 20616 20612 0 17:56 ? 00:00:00 postgres: writer processpostgres 20617 20612 0 17:56 ? 00:00:00 postgres: stats collector processpostgres 20819 20612 0 18:00 ? 00:00:00 postgres: wal writer processpostgres 20820 20612 0 18:00 ? 00:00:00 postgres: autovacuum launcher processpostgres 20821 20612 0 18:00 ? 00:00:00 postgres: archiver process last was 00000008.historypostgres 20822 20612 0 18:00 ? 00:00:00 postgres: bgworker: logical replication launcherpostgres 20832 20612 0 18:00 ? 00:00:00 postgres: wal sender process repliuser 192.168.56.36(45827) streaming 0/440001A8root 21481 16868 0 18:16 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto postgres[root@pgserver2 tmp]# |
And let’s execute the kill command
|
1
|
[root@pgserver2 tmp]# kill -9 20612 |
If we check the cluster status from the witness server, we can see that the master is in an UNKNOWN status
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/efm cluster-status efmCluster Status: efmVIP: Agent Type Address Agent DB Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Witness 192.168.56.30 UP N/A Standby 192.168.56.36 UP UP Idle 192.168.56.37 UP UNKNOWNAllowed node host list: 192.168.56.36 192.168.56.37 192.168.56.30Membership coordinator: 192.168.56.30Standby priority host list: 192.168.56.36Promote Status: DB Type Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Standby 192.168.56.36 0/440001A8 No master database was found.Idle Node Status (idle nodes ignored in XLog location comparisons): Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- 192.168.56.37 UNKNOWN Connection to 192.168.56.37:5436 refused. Check that the hostname and port are correct and that the postmaster is accepting TCP/IP connections.[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# |
In the alert log in our standby server pgserver1, we can see that that the database is converted to a primary one a few time after.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
2018-03-06 18:17:49.381 CET [18384] FATAL: could not receive data from WAL stream: server closed the connection unexpectedly This probably means the server terminated abnormally before or while processing the request.2018-03-06 18:17:49.382 CET [18380] LOG: invalid record length at 0/440001A8: wanted 24, got 02018-03-06 18:17:49.387 CET [19049] FATAL: could not connect to the primary server: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server running on host "192.168.56.37" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5436?2018-03-06 18:17:54.404 CET [19055] FATAL: could not connect to the primary server: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server running on host "192.168.56.37" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5436?2018-03-06 18:17:59.406 CET [19107] FATAL: could not connect to the primary server: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server running on host "192.168.56.37" and accepting…….…. TCP/IP connections on port 5436? TCP/IP connections on port 5436?2018-03-06 18:18:34.450 CET [19128] FATAL: could not connect to the primary server: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server running on host "192.168.56.37" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5436?2018-03-06 18:18:39.451 CET [19134] FATAL: could not connect to the primary server: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server running on host "192.168.56.37" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5436?2018-03-06 18:18:44.462 CET [19135] FATAL: could not connect to the primary server: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server running on host "192.168.56.37" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5436?2018-03-06 18:18:49.456 CET [18380] LOG: trigger file found: /tmp/postgresql.trigger2018-03-06 18:18:49.456 CET [18380] LOG: redo done at 0/440001702018-03-06 18:18:49.479 CET [18380] LOG: selected new timeline ID: 92018-03-06 18:18:50.128 CET [18380] LOG: archive recovery complete2018-03-06 18:18:50.229 CET [18378] LOG: database system is ready to accept connections |
What we can confirm by querying the cluster status
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/efm cluster-status efmCluster Status: efmVIP: Agent Type Address Agent DB Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Witness 192.168.56.30 UP N/A Master 192.168.56.36 UP UP Idle 192.168.56.37 UP UNKNOWNAllowed node host list: 192.168.56.36 192.168.56.37 192.168.56.30Membership coordinator: 192.168.56.30Standby priority host list: (List is empty.)Promote Status: DB Type Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Master 192.168.56.36 0/440002B8 No standby databases were found.Idle Node Status (idle nodes ignored in XLog location comparisons): Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- 192.168.56.37 UNKNOWN Connection to 192.168.56.37:5436 refused. Check that the hostname and port are correct and that the postmaster is accepting TCP/IP connections.[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# |
and
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# /usr/edb/efm-3.0/bin/efm cluster-status efmCluster Status: efmVIP: Agent Type Address Agent DB Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Witness 192.168.56.30 UP N/A Master 192.168.56.36 UP UPAllowed node host list: 192.168.56.36 192.168.56.37 192.168.56.30Membership coordinator: 192.168.56.30Standby priority host list: (List is empty.)Promote Status: DB Type Address XLog Loc Info -------------------------------------------------------------- Master 192.168.56.36 0/440002B8 No standby databases were found.[root@pgservertools efm-3.0]# |
On the old primary pgserver2 we can see the contents of the file recovery.conf automatically created by EDB Failover manager
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
[postgres@pgserver2 101]$ cat recovery.conf# EDB Failover Manager# This generated recovery.conf file prevents the db server from accidentally# being restarted as a master since a failover or promotion has occurredstandby_mode = onrestore_command = 'echo 2>"recovery suspended on failed server node"; exit 1'[postgres@pgserver2 101]$ |
To rebuild our standby database we have to edit the recovery.conf file
Conclusion
We have seen in this blog how to configure edb-efm30. Note that a virtual IP can be also configured. The official documentation can help.
![Thumbnail [60x60]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/oracle-square.png)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/STS_web-min-scaled.jpg)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/STH_web-min-scaled.jpg)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/SNA_web-min-scaled.jpg)