In this part of the blog posts series, we will show how ansible helps us to configure our cluster and install all pre-requisite needed for Cloudera Manager. Ansible is one of the most important automation tools currently.
Ansible will help us to configure all nodes for a manual installation using Cloudera Manager. Our playbook will contain the following roles:
- cm_repo: add the same C.M repo into all nodes.
- os_config: Adjust all OS parameter for installing a Cloudera cluster.
- java: Java JDK 1.7.80 installation.
- cm_agents: Installation of the C.M agent’s packages
- MariaDB: Installation of a MariaDB. C.M needs an Oracle, MySQL (MariaDB) or PostgreSQL database for Cloudera Manager meta-data storage and Hive meta-store.
- mysql_connector: Installation of the MySQL connector for connecting to MariaDB.
- scm: Install and start the Cloudera Manager Server.
In a Big Data cluster, we split the node into roles.
- Manager: dedicated node for all Cloudera Manager daemons
- Master: NameNode daemon + Secondary NameNode daemon
- Workers: DataNode daemons
The first step is to define the Ansible hosts inventory file. Below my inventory file.
[db_server] manager ansible_host=<manager_ip> id=6 [cdh_manager] manager ansible_host=<manager_ip> id=6 [cdh_master] master ansible_host=<master_ip> id=5 [cdh_worker] worker1 ansible_host=<worker1> id=2 worker2 ansible_host=<worker2> id=3 worker3 ansible_host=<worker3> id=4 [cdh_servers:children] cdh_worker cdh_master cdh_manager [all:vars] ansible_user=centos ansible_ssh_pass=<YOUR_PASSWORD> ansible_sudo_pass=<YOUR_PASSWORD>
We will now, define all variable needed for our roles. Variables are split into roles:
Below the example of variables definition for CDH server instances: cdh_servers.yml
---
db_hostname: "{{ hostvars[groups['db_server'][0]]['inventory_hostname'] }}"
scm_hostname: "{{ hostvars[groups['cdh_manager'][0]]['inventory_hostname'] }}"
cdh_version: 5.14.2
cluster_display_name: cluster_1
# Users and Groups
group:
- dbi
user:
- dbi
# Java variables
java_download_url: http://ftp.osuosl.org/pub/funtoo/distfiles/oracle-java/jdk-7u80-linux-x64.tar.gz
java_download_folder: /usr/java
java_name: "{{java_download_folder}}/jdk1.7_80"
java_archive: "{{java_download_folder}}/jdk-7u80-linux-x64.tar.gz"
# Mysql Java connector
mysql_java: mysql-connector-java-5.1.46
mysql_java_download_url: https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/Connector-J/"{{mysql_java_archive}}"
mysql_java_download_folder: /usr/share/mysql-java/
mysql_java_archive: "{{ mysql_java_download_folder }}/{{ mysql_java }}.tar.gz"
mysql_java_jar: /usr/share/java/mysql-connector-java.jar
Same files will created for database server variable (db_server.yml) and Cloudera Manager server variables (scm_server.yml).
After the variables definition, we can start creating the different roles and their associated tasks.
Cloudera Manager repo
The goal of this role is to add the same C.M repo in all cluster hosts. We will use a template of the repository file.
cloudera-manager.repo.j2
[cloudera-manager]
# Packages for Cloudera Manager, Version 5, on RedHat or CentOS 7 x86_64
name=Cloudera Manager
baseurl=https://archive.cloudera.com/cm5/redhat/7/x86_64/cm/{{cdh_version}}/
gpgkey=https://archive.cloudera.com/cm5/redhat/7/x86_64/cm/RPM-GPG-KEY-cloudera
gpgcheck = 1
cm_repo:
---
- name: Add Cloudera repo
template:
src: ../templates/cloudera-manager.repo.j2
dest: "/etc/yum.repos.d/cloudera-manager{{cdh_version}}.repo"
The definition of the Cloudera Manager version has previously done in the cdh_servers.yml variable file.
OS Configuration
Some requirements are needed before installing a Cloudera cluster. This role will configure all hosts with Cloudera requirements: https://www.cloudera.com/documentation/enterprise/release-notes/topics/rn_consolidated_pcm.html#cmig_topic_4 .
---
- name: Create groups
group:
name: "{{item}}"
state: present
with_items: "{{group}}"
- name: Create user
user:
name: "{{item}}"
shell: /bin/bash
uid: 1050
groups: "{{group}}"
with_items: "{{user}}"
- name: "Build hosts file"
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/hosts
regexp: '.*{{ item }}$'
line: "{{ hostvars[item]['ansible_default_ipv4']['address'] }} {{item}}"
state: present
when: hostvars[item]['ansible_default_ipv4']['address'] is defined
with_items: '{{groups.all}}'
- name: Disable transparent huge page - defrag
shell: echo "never" > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag
- name: Disable transparent huge page - enabled
shell: echo "never" > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
- name: VM swappiness - 1
shell: echo "1" > /proc/sys/vm/swappiness
- name: Set VM swappiness - 2
sysctl:
name: vm.swappiness
value: 1
state: present
- name: Create /data dir
file:
path: /data
state: directory
mode: 0775
owner: dbi
group: dbi
- name: Create file system on volume
filesystem:
fstype: ext4
dev: /dev/xvdb
- name: Mount volume as /data
mount:
name: /data
src: /dev/xvdb
fstype: ext4
opts: defaults,noatime
state: mounted
- name: install the latest version of ntp
yum:
name: ntp
state: latest
- name: install the latest version of nscd
yum:
name: nscd
state: latest
- name: install wget
yum:
name: wget
state: latest
- name: Disable SELinux
selinux:
state: disabled
- name: Reboot for SELinux if needed
command: /sbin/shutdown -r +1
async: 0
poll: 0
Java installation
The Java installation is one of the most complex parts of the installation. First, we need to choose a supported version of JDK. Then we need to be sure that Java has been installed properly in all hosts. The installation tasks is split into the following part:
- Create installation directories: /usr/share/java and /usr/java
- Download Java JDK 1.7.80 which is a supported version for Cloudera Manager
- Unarchive Java JDK
- Fix ownership
- Make Java available for the system with alternatives
- Clean up installation download folder
- Add Java home path by exporting $JAVA_HOME variable
Below the java install tasks.
---
- name: Create directories
file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: directory
with_items:
- "{{ java_download_folder }}"
- "/usr/share/java"
- name: Creates directory
file:
path: "{{ java_download_folder }}"
state: directory
- name: Download Java
get_url:
url: "{{ java_download_url }}"
dest: "{{ java_archive }}"
headers: "Cookie:' gpw_e24=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.oracle.com%2F; oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie'"
validate_certs: no
- name: Unarchive Java archive
unarchive:
src: "{{ java_archive }}"
dest: "{{ java_download_folder }}"
copy: no
- name: Fix ownership
file:
state: directory
path: "{{ java_name }}"
owner: root
group: root
recurse: yes
- name: Make Java available for system with alternatives
command: 'alternatives --install "/usr/bin/java" "java" "{{java_name}}/bin/java" 2'
- name: Clean up Java download
file:
state: absent
path: "{{java_archive}}"
- name: Add java home path
blockinfile:
dest: /etc/profile
block: |
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.7.0_80
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
regexp: "JAVA_HOME"
state: present
MariaDB installation
After installing Java, we can start the installation and configuration of MariaDB database. You can find the entire role for MariaDB installation here.
MySQL connector
MySQL connector installation steps will follow approximatively the same steps as Java installation. All details here.
Cloudera Manager Server installation
The last role of this playbook is the installation of Cloudera Manager server. This role will simply install the Cloudera Manager server package in the cdh_manager host and start the 2 following deamons:
- cloudera-manager-daemons
- cloudera-manager-server
---
- include_vars: ../../../group_vars/db_server.yml
- name: Install the Cloudera Manager Server Packages
yum:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: installed
with_items:
- cloudera-manager-daemons
- cloudera-manager-server
# - name: Prepare Cloudera Manager Server External Database
# command: /usr/share/cmf/schema/scm_prepare_database.sh
# -f
# --host {{ hostvars[db_hostname]['inventory_hostname'] }}
# mysql {{ databases.scm.name }} {{ databases.scm.user }} {{ databases.scm.pass }}
# changed_when: False
- name: Start the Cloudera Manager Server
service:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: restarted
enabled: yes
notify:
- wait cloudera-scm-server
with_items:
- cloudera-scm-server
- cloudera-scm-agent
# Trigger handler to wait for SCM to startup
- meta: flush_handlers
site.yml
After creating all roles, we need to define our site.yml in order to execute all tasks in the desired order.
--- # Cloudera playbook - name: Configure Cloudera Manager Repository become: ansible_become hosts: cdh_servers roles: - cm_repo tags: cm_repo - name: Configure Epel repository become: ansible_become hosts: cdh_servers roles: - epel tags: epel_repo - name: OS Configuration become: ansible_become hosts: cdh_servers roles: - os_config tags: os_config - name: Install Java JDK 7 become: ansible_become hosts: cdh_servers roles: - java tags: java - name: Install MySQL Java Connector become: ansible_become hosts: cdh_servers roles: - mysql_connector tags: mysql_java_connector - name: Install MariaDB and create databases hosts: db_server roles: - mariadb tags: mysql # ############## - name: Install Cloudera Manager Agents hosts: cdh_servers roles: - cm_agents tags: cm_agents - name: Install Cloudera Manager Server hosts: cdh_manager roles: - scm tags: cluster_template
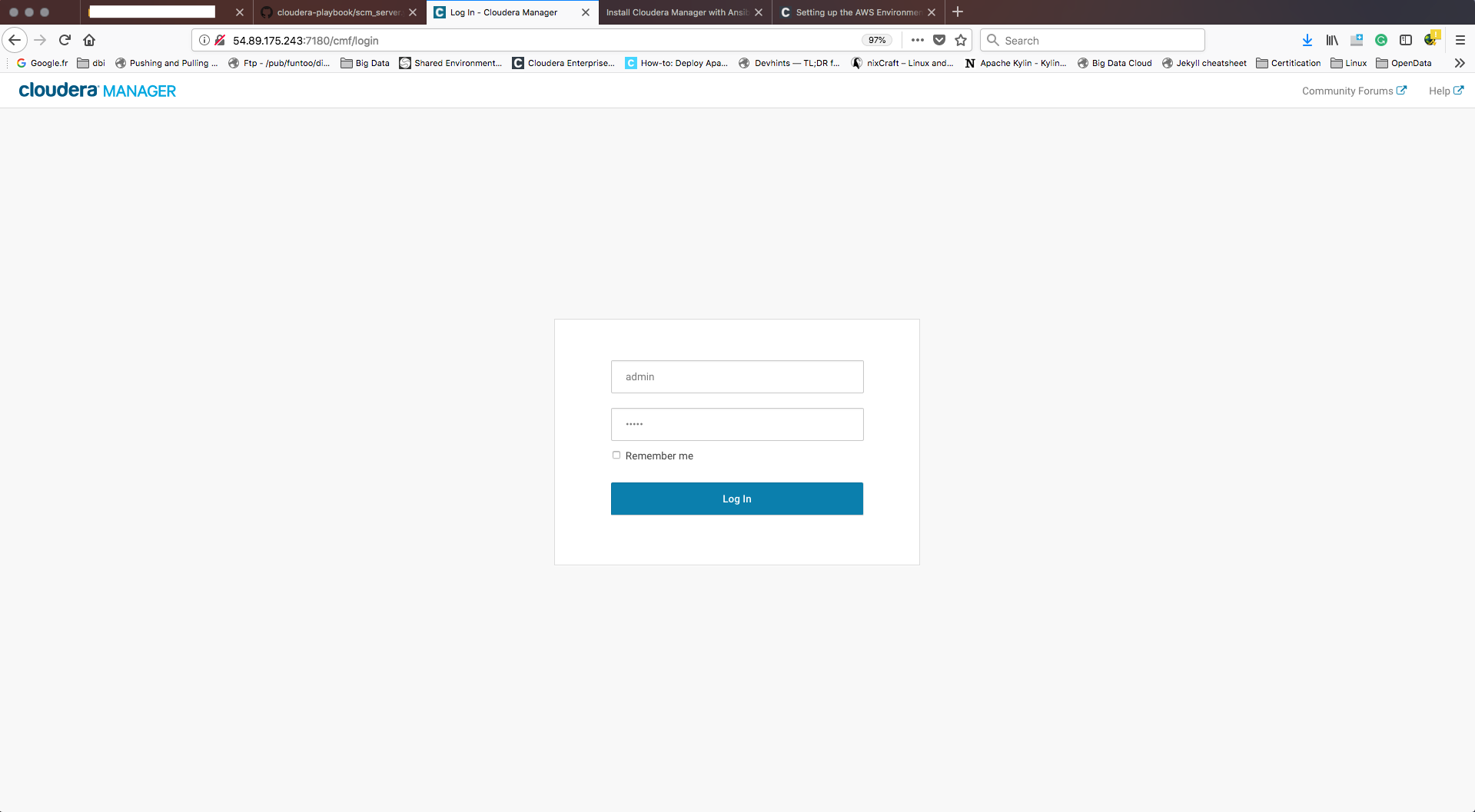
When all steps will finish, you can access to Cloudera Manager web interface by the following:
http://<cdh_manager_ip>:7180
Be sure, your network configuration is well configured to allow access to Cloudera Manager webUI through the default 7180 port.
The entire project with all files is available here.
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/STH_web-min-scaled.jpg)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/DWI_web-min-scaled.jpg)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/HME_web.jpg)