
Cloud-init is a software developed to setup automatically a cloud virtual machine using metadata ingested and applied at the first boot or at a chosen frequency. All the magic happens through a #cloud-config YAML file.
#cloud-config already supports Ansible execution since ages
Yes, true ! But only through cc_runcmd module as follows
#cloud-config
packages:
- git
- ansible
runcmd:
- [ git, clone, <some magic repo URL> ]
- [ ansible-playbook, <magic playbook> ]Alternatively, you can install Ansible through Python package manager (aka. pip)
#cloud-config
packages:
- git
- ansible
runcmd:
- [ python3, -m, pip, install, ansible ]
- [ git, clone, <some magic repo URL> ]
- [ ansible-playbook, <magic playbook> ]Both methods work perfectly fine 🙂
New #cloud-config Ansible module: cc_ansible
Native cloud-init Ansible support offers not only better readability for our YAML file but also a huge operative advantage. As we can now execute, test, validate the execution of the Ansible playbooks in an isolated manner by executing the Ansible playbook as a standalone module:
[root@bastion-openvpn ~]# cloud-init single --name cc_ansible
Cloud-init v. 22.4.2 running 'single' at Wed, 07 Dec 2022 20:48:32 +0000. Up 2457.30 seconds.
Starting Ansible Pull at 2022-12-07 21:48:35
/usr/bin/ansible-pull --url=https://oauth2:<GitHub access token>@github.com/jewdba/Ansible_OpenVPN-server.git playbooks/cloud-init_openvpn-server_setup.yml
PLAY [OpenVPN setup] ********************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [localhost]
TASK [Install eady-rsa package] ************************************************
changed: [localhost]
...Indeed, the cc_ansible module is now available since the release 22.3.x and it goes even beyond a simple Ansible playbook execution.
Please refer to the documentation for details
https://cloudinit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/topics/modules.html#module-cloudinit.config.cc_ansib
#cloud-config an Ansible Control node
# cloud-config
ansible:
install_method: pip
package_name: ansible
run_user: ansible
setup_controller:
repositories:
- path: /home/ansible/
source: <some magic repo URL>
run_ansible:
- playbook_dir: /home/ansible/<magit Ansible project>
playbook_name: <magic playbook>Looks promising isn’t it?
Hint: Checkout the documentation as you might misinterpret some parameters like run_user which works only in case Ansible has been installed with pip (install_method).
#cloud-config an Ansible managed node (ansible-pull)
This paragraph is probably the most interesting as you may want to cloud-init a machine with ansible-pull.
Let’s cloud-init an OpenVPN Rocky Linux 8 server:
#cloud-config
users:
- name: ansible
homedir: /home/ansible
shell: /bin/bash
sudo: 'ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL'
ssh_authorized_keys:
- <SSH plubic key to connect from your laptop>
packages:
- unzip
- epel-release
- git
runcmd:
# fail2ban part of epel-release repo.
- [/usr/bin/dnf, -y, install, fail2ban]
- [/usr/bin/dnf, -y, update, google-osconfig-agent]
- [/usr/bin/dnf, -y, update, google-guest-agent]
- [/usr/bin/systemctl, restart, fail2ban]
write_files:
- path: /etc/fail2ban/jail.d/sshd.conf
permissions: '0640'
owner: root
content: |
[sshd]
enabled=true
# don't block localhost, local machines
ignoreip=127.0.0.1/8 192.168.0.1/16
ansible:
install_method: distro
package_name: ansible.noarch
pull:
#accept_host_key: true
url: "https://oauth2:<GitHub access token>@github.com/jewdba/Ansible_OpenVPN-server.git"
playbook_name: "playbooks/cloud-init_openvpn-server_setup.yml"Quite clear isn’t it?
Almost the perfect combo
It’s definitively worth to invest some time of debugging in order to get everything done by cloud-init and the new cc_ansible module 🙂
Hereby some learnings which may help you to gain/save time:
- RTFM ! Read the manual at least twice ! Especially, for the run_user parameter
(only taken in account if install_method is set to pip)
- Sometimes it’s easier to look at the source code of cc_ansible to understand what is documented (It’s unfortunately well known in the community)
https://github.com/canonical/cloud-init/blob/main/cloudinit/config/cc_ansible.py
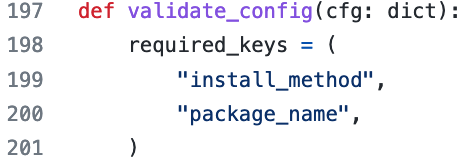
- Don’t trust the documentation examples 🙂 You need to set install_method and package_name whatever the chosen installation method.
Hereby, the proof (snippet of cc_ansible python module)
- Pay attention to the Ansible installation method (parameter install_method) and the tools you want to install (package_name) ! Depending, on your needs the ansible-core package may not be enough.
- Use the exact package name while using native package manager of distrubution (install_method: distro) !
- Last one but not least, run_user parameter does only apply to ansible command lines tools.
The git repo checkout/clone is executed as root
Have fun with #Ansible and #cloud-init
Of course, the Ansible playbooks must be production grade upfront any cloud-init trials
![Thumbnail [60x60]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/JEW_web-min-scaled.jpg)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/martin_bracher_2048x1536.jpg)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/SIT_web.png)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/AHI_web.jpg)