by Alexandre Nestor
Introduction
Oracle Data Redaction is part of Oracle Advanced Security which is well known for Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) for columns and tablespaces.
There is a confusion between Data Redaction and Data Masking:
- Data Redaction is the process to hide (or replace with a defined value) critical informations
- Data Masking is the process to replace critical information with another data, which keep the database structure identical, or at least try to keep database structure identically. Data Masking is an extra cost licence named Data Masking and Subsetting Pack.
To make it easier:
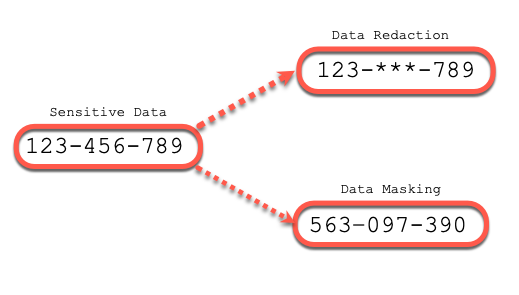
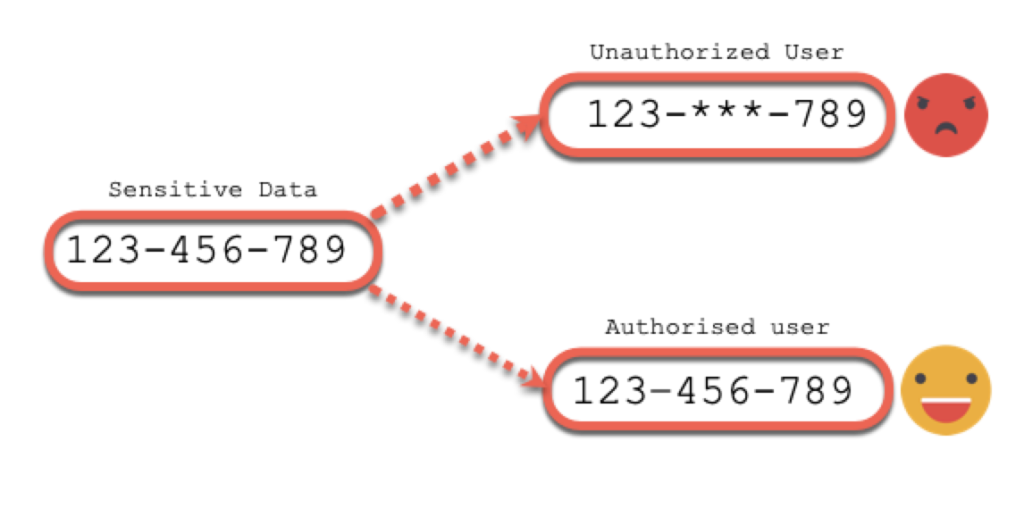
So, we are going to make an example of Data Redaction implementation. Data Redaction do not change the data in the database, it just modify the output following the criteria (user is the mot usual) :
About the rights
To manage Data Redaction policies the are EXECUTE right on DBMS_REDACT package must be granted (or use SYS user to make it easier).
Good to know that granting the EXEMPT REDACTION POLICY system privilege to an user, make the user to bypass the redaction policy.
Let’s build the test environment.
DATA_REDACT.SQL
To make life easier I created a little script to list available policies:
-- data_redact.sql
set lines 110
set pages 9999
col policy_name format a30
col expression format a40
col enable format a8
col object_owner format a19
col object_name format a20
col column_name format a15
col function_type format a25
prompt ===== Current Data Redaction policies
select policy_name, expression, enable from redaction_policies;
prompt
prompt ===== Current Objects redacted by a Data Redaction policy
select object_owner, object_name, column_name, function_type from redaction_columns;
The test table
For the test purpose I create a test table named user_info, an user hr who owns the user_info table, and an user check_user which has the rights to read the user_info table.
-- all commands are executer in a PDB as SYS user.
SQL> alter session set container=PDB01;
Session altered.
-- create the check_user
SQL> create user check_user identified by check_usr;
SQL> grant create session to check_user ;
-- create the hr user who owns the test table user_info
SQL> create user HR identified by hr;
SQL> grant create session to hr ;
SQL> grant resource to hr ;
SQL> alter user hr quota unlimited on users;
SQL> create table user_info(
user_id number,
name varchar2(20),
sn varchar2(20),
corp_card varchar(20),
dt date);
SQL> grant select on user_info to check_user;
Let’s populate the user_info table with some random values:
SQL> declare
type array_t is varray(20) of varchar2(10);
array array_t := array_t('James','Mary','Robert','Patricia','John','Jennifer','Michael','Linda','David','Elizabeth','William','Barbara','Richard','Susan','Joseph','Jessica','Thomas','Sarah', 'Alex', 'Thomas');
begin
for i in 1..array.count loop
insert into user_info values(
trunc(dbms_random.value(low => 1, high => 900)),
array(i),
to_char(trunc(dbms_random.value(low => 100, high => 900)))||'-'||to_char(trunc(dbms_random.value(low => 100, high => 900)))||'-'||to_char(trunc(dbms_random.value(low => 100, high => 900))),
dbms_random.string('x',20),
sysdate + dbms_random.value(0,366)
);
end loop;
commit;
end;
/
SQL> alter session set nls_date_format='DD/MM/YYYY HH24:MI:SS';
SQL> SQL> select * from user_info;
USER_ID NAME SN CORP_CAR DT
---------- -------------------- --------------- -------------------- ---------------
122 James 241-406-613 AWNMDMC21PHHETCG2YKW 19/07/2024 20:51:07
244 Mary 845-527-442 PVQJBY6FGXJO3CYZX2EW 27/07/2024 10:16:47
169 Robert 827-523-178 NSGB6QLJCXYB8H6F12WP 24/04/2024 04:52:44
40 Patricia 796-595-337 JX4FYTJIZN5W10AHMELG 20/01/2024 05:47:45
318 John 175-486-737 DLYEPYCEFMOF3VWLG4J6 17/08/2024 00:49:32
461 Jennifer 672-341-335 V78PSCBPECIIUD2RKG36 14/04/2024 12:28:20
218 Michael 787-680-888 C2L73OG5MFQOP501XLQA 29/07/2024 20:38:29
201 Linda 670-104-321 WWY50UJABZGZ6JZY8J38 06/09/2024 23:39:16
556 David 427-645-834 OX2FZMZI59OBOXRP4PCK 02/12/2023 00:35:16
808 Elizabeth 768-321-407 W0BEYTKV8GU5AT4POH8W 09/08/2024 10:50:49
864 William 634-730-555 CMBI72T3REKT31I55U7K 01/10/2024 00:18:32
751 Barbara 399-768-748 XLSY6HDYPH0NPC88Q4X6 09/02/2024 14:30:01
740 Richard 615-173-203 ATI5E5KWB58AGQ41UQQU 08/04/2024 06:55:50
352 Susan 567-366-498 017HW2WLGCVJJMS5V0SY 07/04/2024 09:44:36
707 Joseph 859-626-829 161OGSUJCV2MTXLK6Z9R 26/09/2024 20:28:10
899 Jessica 602-703-601 CRDA5X3EIKIOFZPRL5FP 25/08/2024 12:46:04
418 Thomas 260-715-289 4MYAOOIS1QXRNQEN5HDL 02/03/2024 15:58:15
859 Sarah 564-447-263 JR3YEKWZ8FLRXBM9M7NG 25/01/2024 14:48:30
223 Alex 345-843-155 CQ5COC6PDM23O1ZDDENP 04/03/2024 18:14:25
370 Thomas 186-555-284 P4TQ4M3T3Q886XT8U0ZO 20/02/2024 23:24:51
The policy creation and management
Commands are executed at PDB level.
SQL> show con_name;
CON_NAME
------------------------------
PDB01
SQL> show user
USER is "SYS"
--- initial state: no config
SQL> @data_redact.sql
====== Current Data Redaction policies
no rows selected
===== Current Objects redacted by a Data Redaction policy
no rows selected
-- Create the policy "PROTECT_EMPLOYEES" for the table "HR.USER_INFO"
SQL> BEGIN
DBMS_REDACT.ADD_POLICY (
object_schema => 'HR'
,object_name => 'USER_INFO'
,policy_name => 'PROTECT_EMPLOYEES'
,expression => '1=1');
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Now we add the SN column to be protected by the policy.
SQL> show con_name;
CON_NAME
------------------------------
PDB01
SQL> show user
USER is "SYS"
SQL> BEGIN
DBMS_REDACT.ALTER_POLICY (
OBJECT_SCHEMA => 'HR'
,object_name => 'USER_INFO'
,policy_name => 'PROTECT_EMPLOYEES'
,action => DBMS_REDACT.ADD_COLUMN
,column_name => 'SN'
,function_type => DBMS_REDACT.FULL );
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- and print the current configuration
SQL> @data_redact.sql
====== Current Data Redaction policies
POLICY_NAME EXPRESSION ENABLE
-------------------- --------------------- --------
PROTECT_EMPLOYEE 1=1 YES
===== Current Objects redacted by a Data Redaction policy
OBJECT_OWNER OBJECT_NAME COLUMN_NAME FUNCTION_TYPE
--------------- -------------------- --------------- -------------------------
HR USER_INFO SN FULL REDACTION
The expression 1=1 (always TRUE) the whole SN column will be hidden.
All users are concerned by the policy, even HR.
[oracle]$ sqlplus hr/hr@myserv:1521/pdb01
SQL> alter session set nls_date_format='DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS';
SQL> select * from hr.user_info where user_id = 774;
USER_ID NAME SN CORP_CARD DT
---------- -------------------- ---------- -------------------- ----------------
774 Patricia WJRAZENFM4JTE2EPSAHU 20-NOV-2024 20:49:36
[oracle@]$ sqlplus check_user/check_user@myserv:1521/pdb01
SQL> alter session set nls_date_format='DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS';
SQL> select * from hr.user_info where user_id = 774;
USER_ID NAME SN CORP_CARD DT
---------- -------------------- ---------- -------------------- ----------------
774 Patricia WJRAZENFM4JTE2EPSAHU 20-NOV-2024 20:49:36
- The SN column is completely hidden
- Once the policy created it is active immediately. No need to restart the database.
- Data Redaction is included in Oracle. No need to make any additional configuration.
- No need to restart user session either.
Let’s give the rights to HR user to see his data now:
SQL> show con_name
CON_NAME
------------------------------
PDB01
SQL> show user
USER is "SYS"
SQL> BEGIN
DBMS_REDACT.ALTER_POLICY (
OBJECT_SCHEMA => 'HR'
,object_name => 'USER_INFO'
,policy_name => 'PROTECT_EMPLOYEES'
,action => DBMS_REDACT.MODIFY_EXPRESSION
,expression => 'sys_context(''userenv'',''session_user'') != ''HR'''
);
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> @data_redact.sql
====== Current Data Redaction policies
POLICY_NAME EXPRESSION ENABLE
-------------------- ---------------------------------------- --------
PROTECT_EMPLOYEE sys_context('userenv','session_user') != 'HR' YES
===== Current Objects redacted by a Data Redaction policy
OBJECT_OWNER OBJECT_NAME COLUMN_NAME. FUNCTION_TYPE
------------------- -------------------- --------------- -------------------------
HR USER_INFO SN FULL REDACTION
-- hr user can see the data
[oracle@]$ sqlplus hr/hr@myserv:1521/pdb01
SQL> select * from hr.user_info where user_id = 774;
USER_ID NAME SN CORP_CAR DT
---------- -------------------- -------------------- -------------------- ---------
774 Patricia 251-336-866 WJRAZENFM4JTE2EPSAHU 20-NOV-24
SQL> exit;
-- others users (check_user) cannot see the data
[oracle@]$ sqlplus check_user/check_user@myserv:1521/pdb01
SQL> select * from hr.user_info where user_id = 774;
USER_ID NAME SN CORP_CAR DT
---------- -------------------- -------------------- -------------------- ---------
774 Patricia WJRAZENFM4JTE2EPSAHU 20-NOV-24
Change the way data is printed on SN column (from 251-336-866 to 251-***-866)
SQL> show con_name
CON_NAME
------------------------------
PDB01
SQL> show user
USER is "SYS"
SQL> BEGIN
DBMS_REDACT.ALTER_POLICY (
OBJECT_SCHEMA => 'HR'
,object_name => 'USER_INFO'
,policy_name => 'PROTECT_EMPLOYEES'
,action => DBMS_REDACT.MODIFY_COLUMN
,column_name => 'SN'
,function_type => DBMS_REDACT.PARTIAL,
function_parameters => 'vvvfvvvfvvv,vvv-vvv-vvv,#,4,6'
);
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
[oracle@]$ sqlplus check_user/check_user@myserv:1521/pdb01
SQL> set line 200
SQL> select * from hr.user_info where user_id = 774;
USER_ID NAME SN CORP_CAR DT
---------- -------------------- -------------------- -------------------- ---------
774 Patricia 251-###-866 WJRAZENFM4JTE2EPSAHU 20-NOV-24
Now add the date field to the policy and change the date to 01-Jan-01:
SQL> show con_name
CON_NAME
------------------------------
PDB01
SQL> show user
USER is "SYS"
SQL> BEGIN
DBMS_REDACT.alter_policy (
object_schema => 'HR',
object_name => 'USER_INFO',
policy_name => 'PROTECT_EMPLOYEES',
action => DBMS_REDACT.MODIFY_COLUMN,
column_name => 'DT',
function_type => DBMS_REDACT.PARTIAL,
function_parameters => 'm1d1y2001h0m0s0'
);
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
[oracle@ ]$ sqlplus check_user/check_user@myserv:1521/pdb01
SQL> set line 200
SQL> select * from hr.user_info where user_id = 774;
USER_ID NAME SN CORP_CAR DT
---------- -------------------- -------------------- -------------------- ---------
774 Patricia 251-###-866 WJRAZENFM4JTE2EPSAHU 01-JAN-01
At the end let’s drop the policy revert all:
SQL> show con_name
CON_NAME
------------------------------
PDB01
SQL> show user
USER is "SYS"
SQL> BEGIN
DBMS_REDACT.DROP_POLICY (
OBJECT_SCHEMA => 'HR'
,object_name => 'USER_INFO'
,policy_name => 'PROTECT_EMPLOYEES');
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
[oracle@]$ sqlplus check_user/check_user@myserv:1521/pdb01
SQL> set line 200
SQL> select * from hr.user_info where user_id = 774;
USER_ID NAME SN CORP_CAR DT
---------- -------------------- -------------------- -------------------- ---------
774 Patricia 251-336-866 WJRAZENFM4JTE2EPSAHU 20-NOV-24
Conclusion
Data Redaction is easy to activate and use. SYS and users who have the EXEMPT REDACTION POLICY privilege, all of the Data Redaction policies are bypassed, so the results of their queries are not redacted.
Once the policy created it is active immediately. No need to restart the database.
Data Redaction is included in Oracle. No need to make any additional configuration.
No need to restart user session either.
Data redaction is included in Oracle Advanced Security license.
![Thumbnail [60x60]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/oracle-square.png)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/SIT_web.png)
![Thumbnail [90x90]](https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/JDE_Web-1-scaled.jpg)